Check out the new MinnowBoard.org website for the most up-to-date information on the MinnowBoard Turbot and the MinnowBoard.org Community.
UEFI
>>>Refer to Update The Firmware tutorial on the new MinnowBoard.org website.
MinnowBoard MAX comes with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) firmware installed. UEFI is a standard firmware interface for PCs, designed to replace the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) by addressing a number of legacy support limitations of BIOS. When the MinnowBoard MAX (or any PC for that matter) starts, the firmware interface controls the booting process, and then passes control to the operating system.
Before working with the MinnowBoard MAX and installing an OS, check the firmware version on your board; if it's not the most current one available, download and update the firmware. Read about how to do this on the MinnowBoard MAX HW Setup page in this wiki.
Intel's firmware website has pre-built 32-bit and 64-bit binary images ready for download and installation. It also offers instruction for obtaining the open source code, binary modules, and tools (for both Windows and Linux) to do your own firmware build.
The UEFI Shell is an interactive BIOS extension that provides an environment for running programs (such as the firmware updater), and interpreting executable script files. Similar to MS-DOS or a Linux command line, there are built-in commands for file manipulation, driver management, device access, BIOS status, scripting control and more. Use help -b for a list of these commands, or see our Shell Commands page.
Contents
- 1 BIOS Menu
- 2 UEFI and EDK II References
- 3 UEFI Version
- 4 Updating
- 5 32-bit vs. 64-bit UEFI
- 6 UEFI Shell
- 7 TPM Support
- 8 BIOS menu
- 9 BIOS Menu Tree
- 9.1 Continue
- 9.2 Select Language
- 9.3 Boot Manager
- 9.4 Device Manager
- 9.5 Boot Maintenance Manager
BIOS Menu
The BIOS menu provides a more traditional way to view and configure basic firmware parameters on the system, set the GPIO pinmux states, and perform the typical tasks one would expect. Access the BIOS menu by pressing F2 or ESC during boot, right after powering the board. If you wait too long to press a key, you may end up in the UEFI Shell environment; enter the exit command to get back to the BIOS menu. You should now be at a screen that looks like this:
This menu provides options to
- change the language (English and French are available),
- select a source of bootable media, such as installing or booting an OS from a USB drive, and
- view detailed platform information, such as processor type, speed, stepping, cores and total memory.
Use the up and down arrows and the Enter key to navigate to the Device Manager/System Setup/Main menu where you'll see something like this:
This MinnowBoard MAX has 2 cores and uses an Intel® Atom™ E3825 CPU @ 1.33 GHz. Use the ESC key to return to the previous screen(s).
Familiarize yourself with the effects of changing an option before doing so in an operation-sensitive context. For example, you may disable the integrated graphics display (IGD) in the Device Manager/System Setup/Uncore Configuration menu, but when rebooting the board, the only way to see output and turn IDG back on is via the serial port.
A few notes about specific settings:
- Device Manager/System Setup/South Cluster Configuration/LPSS & SCC Configuration
- LPSS & SCC Devices Mode should be set to <ACPI Mode>
- LPSS HSUART #2 does not have hardware FlowControl because CTS/RTS lines are not pulled out
UEFI and EDK II References
Intel provides more information about its firmware development kit, EDKII, which contains everything you need to develop UEFI firmware applications or drivers for the MinnowBoard MAX. See the below URLs:
UEFI Version
Publicly released versions
- http://firmware.intel.com/projects/minnowboard-max : All Max/Turbot releases posted here.
How to tell your firmware version
- Get to the UEFI menu
- Either boot to the UEFI shell and type:
Shell> exit - Hit F2 during boot
- Either boot to the UEFI shell and type:
- The 3rd line down will be the firmware version
- will look something like:
MNW2CRB1.X64.0071.R30.1408131301
- will look something like:
Decoding the Version String
| MNW2CRB1 | X64 | 0071 | R30 | 1408131301 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmware Type
MinnowBoard MAX (v2) CRB1 |
Architecture 32-bit vs. 64-bit I32 = 32-bit X64 = 64-bit |
Version Number | Firmware Type
R30 R = Release D = Debug |
Build number
YYMMDDHHMMSS YY = Year MM = Month DD = Day HH = Hour MM = Minute SS = Second |
Updating
This is a VERY abbreviated version of the updating process, you should refer to the official documentation (that is unfortunately contained in a zip file) at http://firmware.intel.com/sites/default/files/MinnowMax_documentation.zip
- take a fat32 usb stick, unzip and copy the two files in the zip to that.
- boot up the MinnowBoard MAX without any other storage installed. This should get you to the UEFI shell. If that doesn't work hit F2 while booting and use the boot manager to select the efi shell
- at the shell type:
fs0: FirmwareUpdate.efi MNW2_IFWI_X64_D_2014_07_18_1654_SecEnabled.bin
Tab completion works, as well as you want to check what the you are on the right drive.
This will run for a while, and will shut the board down. Just power it back on (pressing SW1 should power it back up) and you are done, the board is usable normally.
EFI partition based "auto" updater
For anyone interested, it is possible to run a script, in an automated fashion, that will update the firmware. I'm going to leave the below startup.nsh script here for anyone interested in taking a look. The basic idea is that the system will default (if all else fails) to running startup.nsh, within this script is a setup that should update the firmware and the machine halt:
startup.nsh: ------------ MinnowBoard.MAX.FirmwareUpdateX64.efi fs0:\MinnowBoard.MAX.X64.90.R01.bin
that has an example filesystem hierarchy of:
. ├── EFI │ └── BOOT │ ├── bootx64.efi │ └── grub.cfg ├── MinnowBoard.MAX.0.90.BIN-ReleaseNotes.txt ├── MinnowBoard.MAX.FirmwareUpdateX64.efi ├── MinnowBoard.MAX_.FirmwareUpdateX64.zip ├── MinnowBoard.MAX.X64.90.R01.bin ├── MinnowBoard.MAX_.X64.90.R01.zip └── startup.nsh
32-bit vs. 64-bit UEFI
UEFI, our primary boot firmware, is very different than a traditional BIOS or even the firmware in other non-x86 embedded systems. It is more commonly found in servers, desktops and laptops, which has advantages and disadvatnages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
One of the things in the specification defines is that a 64-bit OS will have a 64-bit firmware, a 32-bit OS will have a 32-bit firmware. This is a HUGE change from the traditional BIOS perspective, which could and did handle both simultaneously. This isn't a huge difference from most of the embedded world, as there hasn't been a lot of hardware that supports both 32-bit and 64-bit.
But to be very clear here:
Support matrix of firmware and OS:
| 32-bit Firmware | 64-bit Firmware | |
|---|---|---|
| 32-bit OS | Supported | UNSupported |
| 64-bit OS | UNSupported | Supported |
Running in an unsupported configuration may not even boot, but at the least will lead to very odd system interactions. Having a single firmware with UEFI that supports both is not possible.
UEFI Further reading
Switching from 64-bit to 32-bit
- Verify you are on a 64-bit Firmware
- Boot the MinnowBoard MAX, hitting F2 or at the UEFI shell typing
Shell> exit - Look at the 3rd line on the screen, it should say something similar to:
MNW2MAX1.X64.0073.R02.1409031643 - Verify that the second grouping says X64. If it says I32 you have a 32-bit firmware, please skip down to the next section if you want to convert back to 64-bit
- Boot the MinnowBoard MAX, hitting F2 or at the UEFI shell typing
- Snag a copy of the firmware you want to use from:
- https://firmware.intel.com/projects/minnowboard-max
- Verify that the firmware you downloaded has X32 in the firmware name
- Unzip the firmware to somewhere convenient
- Using the FirmwareUpdateX64.efi flash the 32-bit firmware
- the X64 in this case refers to the efi program you are running *NOT* to the firmware itself
Switching from 32-bit to 64-bit
- Verify you are on a 32-bit Firmware
- Boot the MinnowBoard MAX, hitting F2 or at the UEFI shell typing
Shell> exit - Look at the 3rd line on the screen, it should say something similar to:
MNW2MAX1.I32.0073.R02.1409031643 - Verify that the second grouping says I32. If it says X64 you have a 64-bit firmware, please skip down to the previous section if you want to convert back to 32-bit
- Boot the MinnowBoard MAX, hitting F2 or at the UEFI shell typing
- Snag a copy of the firmware you want to use from:
- https://firmware.intel.com/projects/minnowboard-max
- Verify that the firmware you downloaded has X64 in the firmware name
- Unzip the firmware to somewhere convenient
- Using the FirmwareUpdateIA32.efi flash the 64-bit firmware
- the IA32 in this case refers to the efi program you are running *NOT* to the firmware itself
UEFI Shell
The simplest way to get to the UEFI shell is to:
- Make sure that the MinnowBoard MAX is powered down
- Disconnect all bootable media
- USB drives
- SATA drives
- SD cards
- Power on the MinnowBoard MAX
At this point you should get a screen that looks very similar to the one at right. This is the UEFI Shell, there are a number of commands that can be done here, and the system can be explored in great depth from this interface.
Places to find more information about UEFI shell and it's commands:
- https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/uefi-shell
- http://www.sysadminshare.com/2012/01/efi-shell-commands.html
No bootable devices found
If you boot to the UEFI shell and you get the following (or similar)
EFI Shell version 2.40 [1.0] Current running mode 1.1.2 map: Cannot find required map name. Press ESC in 1 seconds to skip startup.nsh, any other key to continue. Shell>
Then your boot, for some reasons, failed to detect any bootable media attached. Double check your connections and then run:
Shell> connect -r Shell> map -r
If that doesn't work, reboot.
TPM Support
The firmware ships with a Firmware TPM (FTPM) built into it. This is mainly for use with OSes that need a TPM, while leaving the room for the board to still be fully resetable.
There is support for external, hardware, TPMs if interested:
http://d.hatena.ne.jp/munetoh/20160904/ has a lot of good information collected
There's also a good HOWTO video available at https://software.intel.com/en-us/videos/use-discrete-tpm-2-0-moduleon-minnowboard-turbot
The BIOS menu gives a more traditional way to configure the basic firmware parameters on the system, set the GPIO pinmux states and perform the typical tasks one would expect to do in these menus.
To get to it:
- Key-press way
- Press F2 during bootup to jump directly to it. Prior to powering on the board, start holding down F2, and continue holding it down until you see the BIOS menu. This will not work over the serial console, it's necessary to actually plug a keyboard into the Minnowboard Max.
- UEFI Shell way
- Follow the steps to get to the UEFI Shell (above)
- Type the following:
exit
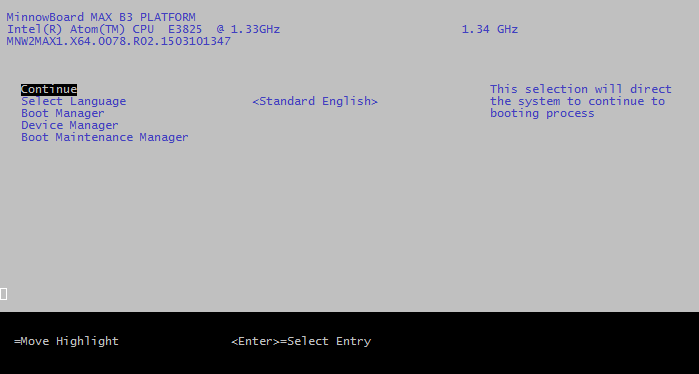
You should now get a screen that looks like the following: Main BIOS menu screen
This is the main menu on the BIOS menu
BIOS Menu Tree
Continue
This just continues the boot process
Select Language
This adjusts the language that the bios is displayed in
Boot Manager
This adjusts the basic boot options, including what to boot to.
EFI Internal Shell
This will boot to the UEFI shell
Device Manager
This allows for the configuration of specific devices on the system
System Setup
Configure System Settings
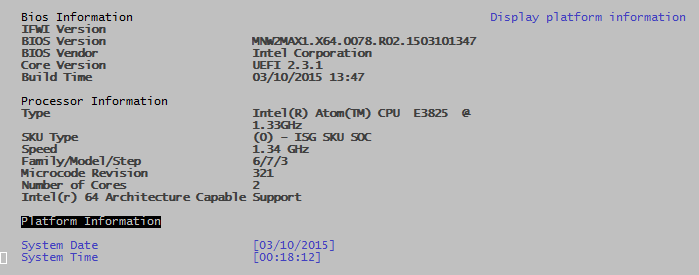
Main
Contains:
- Bios Information
- IFWI Version
- BIOS Version
- BIOS Vendor
- Core Version
- Build Time
- Processor Information
- Type
- SKU Type
- Speed
- Family/Model/Step
- Microcode Revision
- Number of Cores
- 64-bit capability
- System Date
- System Time
Platform Information
- Platform firmware Information
- VLV SOC
- MRC Version
- PUNIT FW Patch
- PMC FW Patch
- KSC FW
- TXE FW Version
- GOP
- CPU Flavor
- Board ID
- Fab ID
- Memory Information
- Total Memory
- Memory Speed
- L1 Data Cache
- L1 Instruction Cache
- L2 Cache RAM
CPU Configuration
Hyperthreading Supprt: (Chip doesn't support it)
CPU Power Management
<no options>
Uncore Configuration
- GOP Configuration
- GOP Driver
Enable / Disable
Enabled: will unload VBIOS; Disabled it will load VBIOS - GOP Brightness Level
20/40/60/80/100/120/140/160/180/200/220/240/255
Sets the GOP brightness
- GOP Driver
- IGD Configuration (Integrated Graphics Device)
- Integrated Graphics Device
Enable / Disable
Enable or disabled the integrated graphics. NOTE: If you disable this, the only way to turn it back on is via the serial port - Primary Display
IGD / Auto / PCIe - RC6 (Render Standby)
Enable / Disable - PAVC
LITE Mode / Disable / SERPENT Mode - DOP CG
Enable / Disable - GTT Size
2MB / 1MB - Aperture Size
256MB / 128MB / 512MB - DVMT Pre-Allocated
64M / 96M / 128M / 160M / 192M / 224M / 256M / 288M / 320M / 352M / 384M / 416M / 448M / 480M / 512M - DVMT Total Gfx Mem
256M / 128M / MAX - IGD Turbo
Auto / Enable / Disable
- Integrated Graphics Device
- IGD - LCD Control
- Force Lid Status
Auto / OFF / ON - BIA
Auto / Disabled / Level 1 / Level 2 / Level 3 / Level 4 / Level 5 - ALS Support
Disable / Enable - LCD Panel Type
Auto / 640x480 / 800x600 / 1024x768 / 1280x1024 / 1366x768 / 1680x1050 / 1920x1200 / 1280x800 - IGD Boot Type
Auto / VGA Port / HDMI / DP Port B / DB Port C / eDP / DSI PORT A / DSI PORT C - Panel Scaling
Auto / Centering / Stretching - GMCH BLC Control
PWM-Inverted / GMBus-Inverted / PWM-Normal / GMBus-Normal
- Force Lid Status
- ISP PCI Device Configuration
- ISP Enable / Disable
Enable / Disable - ISP PCI Device Selection
ISP PCI Device as B0D2F0 / Disable / ISP PCI Device as B0D3F0
- ISP Enable / Disable
South Cluster Configuration
The South Cluster can be thought of like an old south bridge chipset.
PCI Express Configuration
- PCIe 0 Speed
Auto / Gen1 / Gen2
UNUSED - PCIe 1 Speed
Auto / Gen1 / Gen2
UNUSED - PCIe 2 Speed
Auto / Gen1 / Gen2
Gigabit Ethernet - PCIe 3 Speed
Auto / Gen1 / Gen2
High Speed Connector - PCI Express Root Port 1
Enable / Disable - PCI Express Root Port 2
Disable / Enable - PCI Express Root Port 3
Enable / Disable - PCI Express Root Port 4
Disable / Enable
USB Configuration
- USB Controller Auto Mode
Enable / Disable- XHCI Controller
Enable / Disable
NOTE: This series of options is only available if Disable is selected for the previous setting- HSIC #0
Disable / Enable
- HSIC #0
- XHCI Mode
Enable / Disable - USB2 Link Power Management
Enable / Disable
- XHCI Controller
- USB OTG Support
Disable / PCI Mode
NOTE: The Baytrail-I (which the MinnowBoard MAX uses) does not have an OTG capable port - USB VBUS
ON / OFF / Auto - EHCI Controller
Disable / Enable
This is normally greyed out - USB RMH Mode
Enable / Disable
This is normally greyed out - USB EHCI debug
Disable / Enable
This is normally greyed out - USB Per-Port Control
Enable / Disable
This is dependent on USB Controller Auto Mode being disabled - USB Port #0
Enable / Disable
This is dependent on USB Controller Auto Mode being disabled - USB Port #1
Enable / Disable
This is dependent on USB Controller Auto Mode being disabled - USB Port #2
Enable / Disable
This is dependent on USB Controller Auto Mode being disabled - USB Port #3
Enable / Disable
This is dependent on USB Controller Auto Mode being disabled
Audio Configuration
- LPE Audio Support
Disable / LPE Audio PCI mode / LPE Audio ACPI mode
NOTE: Audio is available via I2S, but requires a codec chip to be useful. This is intended to be resolved in a later lure. - Audio Controller
Enable / Disable- Azalia VCi Enable
Enable / Disable - Azalia Docking Support Enable
Disable / Enable - Azalia PME Enable
Enable / Disable - Azalia HDMI Codec
Enable / Disable
- Azalia VCi Enable
SATA Drives
- Chipset-SATA Controller Configuration
- Chipset SATA
Enable / Disable
- Chipset SATA
- SATA Test Mode
Disable / Enable- Chipset SATA Mode
AHCI / IDE- SATA Port 0
[Not Installed]
NOTE: This is the port pinned out, when a drive is present it's name will be populated - SATA Port 1
[Not Installed]
NOTE: Not used, not pulled out from the SOC - SATA Port 0 Hot Plug
Enable / Disable
- SATA Port 0
- Chipset SATA Mode
- Capability
- SATA Port 1 Hot Plug
Enable / Disable
Note: This port is not used on the MinnowBoard MAX
- SATA Port 1 Hot Plug
- Capability
LPSS & SCC Configuration
This is used to configure the various Low-speed pin connections on the MinnowBoard MAX
- LPSS & SCC Devices Mode
PCI Mode / ACPI Mode
- SCC Configuration
- SCC eMMC Boot Controller
Auto Detect / Disable / eMMC 4.41 / eMMC 4.5 - eMMC Secure Erase
Disable / Enable
- SCC eMMC45 Support
Enable / Disable
Greyed out - DDR50 Capability Support
Enable / Disable
Greyed out - HS200 Capability Support
Enable / Disable
Greyed out - Re Tune Timer Value
8
Greyed out
- SCC SDIO Support
Enable / Disable - SCC SD Card Support
Enable / Disable - SDR25 Capability Support for SDCard
Disable / Enable
Greyed out - DDR50 Capability Support for SDCard
Enable / Disable
Greyed out
- LPSS 1 Configuration
- LPSS DMA #1 Support
Enable / Disable - LPSS HSUART #1 Support
Disable / Enable
Note: Controls the state of Low-speed pins #6, #8, #10, #12 - LPSS HSUART #1 FlowCtrl
Enable / Disable
Note: This is only available when HSUART #1 is on - LPSS HSUART #2 Support
Disable / Enable
Note: Controls the state of Low-speed pins #17, #19. HSUART #2 does not have hardware FlowControl due to lack of CTS/RTS lines being pulled out - LPSS HSUART #2 FlowCtrl
Enable / Disable
Note: This is only available when HSUART #2 is on
Note: Hardware Flow Control is not available, since CTS / RTS are not pulled out and available - LPSS PWM #1 Support
Disable / Enable
Note: Controls the state of Low-speed pin #22 - LPSS PWM #2 Support
Disable / Enable
Note: Controls the state of Low-speed pin #24 - LPSS SPI Support
Disable / Enable
Note: Controls the state of Low-speed pins #5, #7, #9, #11
- LPSS 2 Configuration
- LPSS DMA #2 Support
Enable / Disable - LPSS I2C #5 Support
Enable / Disable
Note: This is what's used on the Low-speed pins #13, #15 - LPSS I2C #6 Support
Enable / Disable
Note: This is what's used for the High Speed I2C pins
- I2C Devices Configuration
- I2C Touch Device Address
'Auto / 0x4B / 0x4A
- SAR Sensor
Enable / Disable
ISCT Configuration
Intel Smart Connect Technlogy, this probably doesn't work with the MinnowBoard MAX, your mileage may vary and this is currently untested.
- ISCT Configuration
- ISCT Configuration
Disable / Enable- Options Available upon Enable
- ISCT Notification Control
Enable / Disable - ISCT WLAN Power Control
Enable / Disable - ISCT WWAN Power Control
Disable / Enable - ISCT Sleep Duration Value Format
Seconds - ISCT RF Kill Support
Physical Switch / Soft Switch
Note: The MinnowBoard MAX does not explicitly provide either of these switches, Your Mileage May Vary
- ISCT Notification Control
- Options Available upon Enable
- WLAN Card Presence
- NGFF Card Inserted
NO / YES
Note: The MinnowBoard MAX does not specifically support NGFF - UHPAM Card Inserted
NO / YES
Miscellaneous Configuration
- Miscellaneous Configuration
- High Precision Timer
Enable / Disable - State After G3
S0 State / S5 State - Clock Spread Spectrum
Disable / Enable - UART Interface Selection
Internal UART / SuperIO UART - PCU UART Com 1
Enable / Disable - BIOS Read/Write Protection
Disable / Enable - PCI MMIO Size
2GB / 0.75GB / 1GB / 1.25GB / 1.5GB - PCI Express Dynamic Clock Gating
Disable / Enable
Boot
- Fast Boot
Disable / Enable - UEFI Security Boot
Disable / Enable - Silent Boot
Disable / Enable - BootTime Log
Enable / Disable- Latest BootTime
No Record
Note: Greyed out
- Latest BootTime
Security Configuration
- TXE Configuration
- TXE FW Version
Greyed Out - TXE FW Capabilities
Greyed Out - TXE FW Features
Greyed Out - TXE FW OEM Tag
Greyed Out - TXE Firmware Mode
Greyed Out - TXE Temporary Disable
Greyed Out - TXE File System Integrity Value
- TPM Configuration
- PTT
Disable
Greyed Out - Discrete TPM
Enable / Disable
- Password Setting
- Setup Administrator Password
Text box, no default value - User Password
Text box, no default value
- Intel® Anti-Theft Technology Configuration
- Intel® ATAM
Disable / Enable - Intel® AT Platform PBA
Enable / Disable
Thermal
- Processor Participant
- Critical Trip Piint
90 C / 15 C / 23 C / 31 C / 39 C / 47 C / 55 C / 63 C / 71 C / 79 C / 85 C / 87 C - Passive Trip Point
85 C / 15 C / 23 C / 31 C / 39 C / 47 C / 55 C / 63 C / 71 C / 79 C / 87 C / 90 C
- Active Trip Points
Disable / Enable
- Dynamic Platform & Thermal Framework
- DPTF
Disable / Enable- Enabling DPTF allows for the following options:
- CPU Sensor PArticipants
- Critical
70 C / 25 C / 35 C / 40 C / 45 C / 50 C / 55 C / 60 C / 65 C / 75 C / 80 C / 85 C / 90 C / 95 C / 100 C / 105 C / 110 C / 115 C / 120 C / 125 C - Passive
60 C / 25 C / 35 C / 40 C / 45 C / 50 C / 55 C / 65 C / 70 C / 75 C / 80 C / 85 C / 90 C / 95 C / 100 C / 105 C / 110 C / 115 C / 120 C / 125 C - Ambient Sensor Participants
- Critical
60 C / 25 C / 35 C / 40 C / 45 C / 50 C / 55 C / 65 C / 70 C / 75 C / 80 C / 85 C / 90 C / 95 C / 100 C / 105 C / 110 C / 115 C / 120 C / 125 C - Passive
43 C / 25 C / 35 C / 40 C / 45 C / 50 C / 55 C / 60 C / 65 C / 70 C / 75 C / 80 C / 85 C / 90 C / 95 C / 100 C / 105 C / 110 C / 115 C / 120 C / 125 C - DDR Sensor Participants
- Critical
81 C / 25 C / 35 C / 40 C / 45 C / 50 C / 55 C / 60 C / 65 C / 70 C / 75 C / 80 C / 85 C / 90 C / 95 C / 100 C / 105 C / 110 C / 115 C / 120 C / 125 C - Passive
62 C / 25 C / 35 C / 40 C / 45 C / 50 C / 55 C / 60 C / 61 C / 65 C / 70 C / 75 C / 80 C / 85 C / 90 C / 95 C / 100 C / 105 C / 110 C / 115 C / 120 C / 125 C
- Enabling DPTF allows for the following options:
- Scenario Design Power
- Brand String
N2805/06 / N3510/20 / N2910/20 / N2810/15/20 / J2850/2900 / J1850/1900 / J1750/1800
System Component
- System Power and Performance (PnP) Configuration
- SoC PnP Setting
Auto Detect / Disable / Ax Stepping / Bx Stepping - CFIO/GPIO PnP Setting
Disable / Enable - LPC PnP Setting
Disable / Enable - FSA ON
OFF / ON
Debug Configuration
- ACPI Memory Debug Switch
- ACPI Memory Debug
Enable / Disable
- ExI
Disable / Enable - WITT Configuration
- Enable WITT
Disable / Enable - Enable UTS(Uart Test Suite)
Disable / Enable
- Lakemore Configuration:
- Memory Allocation Size
0 KiB / 16000 KiB / 8000 KiB / 1000 KiB / 128 KiB - PDM/Dfx Setting
PDM On / Perf Mode / Power Save / Debug Reserved - PDM Msg Output
Disable / Main Memory / IO - TBD
- Enable DB2 Table
Enable / Disable
- PM Weights
Enable / Disable
- Disable Codec ALC-262
NO / YES
Secure Boot Configuration
Set Secure Boot information
- Current SecureBoot State
Disabled
Option Greyed Out - Attempt Secure Boot
[ ] / [X] - Secure Boot Mode
Standard Mode / Custom Mode- Custom Secure Boot Options
- PK Options
- Enrolll PK
- Enroll PK Using File
- Delete PK
- Enrolll PK
- KEK Options
- Enroll KEK
- Enroll KEK using File
- Signature GUID
- Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
- Delete KEK
- Enroll KEK
- DB Options
- Enroll Signature
- Enroll Signature Using File
- Signature GUID
- Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
- Delete Signature
- Enroll Signature
- DBX Options
- Enroll Signature
- Enroll Signature Using File
- Signature GUID
- Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
- Delete Signature
- Enroll Signature
- PK Options
- Custom Secure Boot Options
Network Device List
- Network Device List
- MAC:--:--:--:--:--:--
- Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller (MAC:--:--:--:--:--:--)
- Basic information about the Gigabit Ethernet
- IPv4 Network Configuration
- Configured
[ ] / [X]- Enable DHCP
[ ] / [X] - Local IP Address
__ - Local NetMask
__ - Local IP Gateway
__ - Save Changes and Exit
- Enable DHCP
- Configured
- Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller (MAC:--:--:--:--:--:--)
Boot Maintenance Manager
Boot Options
- Go Back To Main Page
Add Boot Option
There will be a list of bootable options here
Delete Boot Option
- EFI Internal Shell
[ ] / [X] - EFI USB Device
[ ] / [X] - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Change Boot Order
- Change the order
<EFI Internal Shell>
<EFI USB Device> - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Driver Options
- Go Back To Main Page
Add Driver Options
- Add Driver Option Using File
Delete Driver Option
- Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Change Driver Order
- Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Console Options
- Go Back To Main Page
Console Input Device Select
- UEFI Path for Serial
[X] / [ ] - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Console Output Device Select
- UEFI Path ACPI Address
[X] / [ ] - UEFI Path Serial Address
[X] / [ ] - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Console Standard Error Device Select
- UEFI Path ACPI Address
[ ] / [X] - UEFI Path Serial Address
[ ] / [X] - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Console Output Mode Select
- Set Console Output Mode
100 x 31 / 80 x 25 - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
COM Attribute Setup Page
- Go Back To Main Page
Set COM Attributes
- Set COM Baud Rate
115200 / 57600 / 38400 / 19200 / 9600 / 7200 / 4800 / 3600 / 2400 / 1800 / 1200 / 600 / 300 / 150 / 134 / 110 / 75 / 50 - Set COM Data Bits
8 / 5 / 6 / 7 - Set COM Parity
None / Even / Odd / Mark / Space - Set COM Stop Bits
One / One and A Half / Two - Set COM Terminal Type
PC_ANSI / VT_100 / VT_100_PLUS / VT_UTF8 - Set COM Flow Control
None / Hardware
- Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Discard Changes and Exit
Boot From File
- UEFI Path
Set Boot Next Value
- Boot Next Value
NONE / EFI Internal Shell / EFI USB Device - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit
Set Time Out Value
- Auto Boot Time-out
[5] / Range: 0-65535 seconds. 0 is no wait, 65535 is wait for key press - Commit Changes and Exit
- Discard Changes and Exit