Check out the new MinnowBoard.org website for the most up-to-date information on the MinnowBoard Turbot and the MinnowBoard.org Community.
MinnowBoard Turbot
>>>For the most up-to-date information on the MinnowBoard Turbot and the MinnowBoard.org Community, see the new MinnowBoard.org website.
Until further notice, MinnowBoard MAX and V1 content is available here on the wiki.
| Differences from MinnowBoard MAX A2 | |
|---|---|
| Category | Feature |
| Core Logic |
|
| Manufactured By: | ADI Engineering |
| Note: These features and specifications may be subject to change without notice. | |
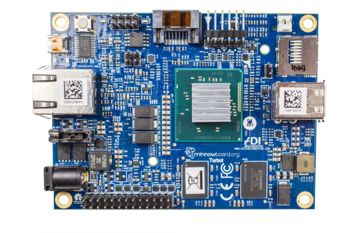
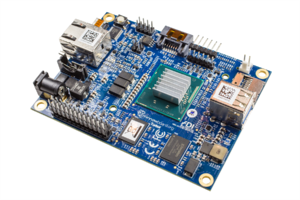
MinnowBoard Turbot is a MinnowBoard MAX-compatible derivative board designed and manufactured by ADI Engineering and includes a number of changes, updates, and fixes that enhance the board's ease-of-use and addresses reported errata. The MinnowBoard Turbot has the same form factor, user connections, connector locations, mounting holes, and High-Speed and Low-Speed Expansion connectors as the MinnowBoard MAX, and runs the same MinnowBoard MAX software. The MinnowBoard Turbot Dual Core is qualified for regulatory compliance (FCC Part 15 Class A, CE Class A, IEC-60950, RoHS/WEEE). The MinnowBoard Turbot B Quad Core is qualified for regulatory compliance (FCC Part 15 Class B, CE Class B, IEC-60950, RoHS/WEEE).
|
|
| MinnowBoard Turbot Dual Core | MinnowBoard Turbot Quad Core |
Specific improvements and additions include:
- Uses a faster Intel®Atom™ SoC
- The Dual Core uses the E3826 SoC(10% higher CPU code speed and 25% higher graphics speed than the E3825 SoC on the MinnowBoard MAX)
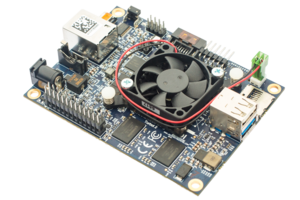
- The Quad Core uses the E3845 SoC
- Populated J2 - Fan Connector
- Note: The fan connector is used by the SoC Fan on the Quad core version
- Populated the Real-time Clock coin-cell battery holder (takes a CR1225 or BR1225 battery)
- Populated J5 - Power Button jumper
- Populated J6 - SATA activity LED
- Populated J7 - GPIO inputs (NVRAM Reset)
- I2S MCLK routed to LSE connector (audio interface)
- Added dedicated I2C shifter
- Low-Speed Expansion connector can now supply power
- D2 LED now under GPIO control
This page lists only MinnowBoard Turbot-specific information. See the MinnowBoard MAX page for information common to both boards.
Contents
Low Speed Expansion Connector (Top)
MinnowBoard MAX LSE information
NOTE: All I/O on the Low Speed Expansion Connector is at 3.3V levels. THE PINS ARE NOT 5v TOLERANT (same for MinnowBoard MAX and MinnowBoard Turbot)
NOTE: The pinout for the LSE on the MinnowBoard Turbot is the same as the MinnowBoard MAX A2 desgin, with the exception of pin 26 (highlighted below). Pin 26 was changed to provide an MCLK reference clock for I2S. Unfortunately this pin is not the same between the MinnowBoard Turbot, the MinnowBoard MAX A2, and the MinnowBoard MAX A4 designs, so care needs to be taken when using this pin.
LSE Layout
NOTE: The definitive layout of these pins is being maintained on the MinnowBoard MAX page.
The Linux GPIO base address changed (by adding 256) from Linux kernel versions 3.17 to 3.18, so you'll need to know which kernel version you're using to select the correct GPIO numbers. This table lists the GPIO number for both the 3.17 and earlier kernels, and 3.18 and later kernels, for each pin on the connector:
| Description | Name | Pin | Linux GPIO# (≤3.17) | Linux GPIO# (≥3.18) | Linux GPIO# (≥3.18) | Linux GPIO# (≤3.17) | Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground | Gnd | 1 | 2 | Gnd | Ground | ||||
| +5V Power | VCC | 3 | 4 | +3V3 | + 3.3V Power | ||||
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . |
| GPIO / Wakeup | GPIO_S5_2 | 25 | 84 | 340 | 509 | 253 | 26 | I2SMCLK_GPIO | I2S MCLK / GPIO |
D2 GPIO LED
On the Turbot, the D2 LED is now GPIO controllable from the operating system. It defaults to the same behavior on the MAX, which is to say on boot-up it indicates that the CPU is running. Once the system is up and running however you may toggle the GPIO as if it was a normal LED via the standard GPIO interfaces. There is no corresponding pin available on the board that also attaches to this (I.E. this is not tied to an LSE pin). For reference, under Linux the GPIO mapping is:
| Description | Name | Linux GPIO# (≤3.17) | Linux GPIO# (≥3.18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D2 LED | D2 LED | 104 | 360 |
A code sample can be found in the Extras repo on github:
https://github.com/MinnowBoard/minnow-max-extras/blob/master/onboard/d2-led.sh
HDMI
Two things have changed with HDMI on the Turbot:
Weak HDMI signal
The weak HDMI signal has been resolved with an appropriate differential pair level shifter.
See Weak HDMI Known Issue for more details
CEC
CEC has been wired up on the Turbot, please see MinnowBoard MAX HDMI CEC for details, including the GPIO it's attached to.
On the Turbot HDMI CEC is plumbed through to the SoC, and is connected to GPIO_S0_SC_58 (which should be Linux GPIO # 212 on older kernels, ≤3.17, and 468 on newer kernels) (NOTE: Always double check pin assignments on the exemplar board's documentation as that's where the definitive answer will be)
Known Issues
MinnowBoard-MAX Open Bugs (Bugzilla)
- Bugzilla:
We currently use the YoctoProject Bugzilla instance at http://bugzilla.yoctoproject.org - Bug Triage link can be found at: https://wiki.yoctoproject.org/wiki/Minnow_Bug_Triage
Weak HDMI signal causing some monitors to not work
This weak HDMI signal issue is explicitly fixed with the MinnowBoard Turbot. See MinnowBoard MAX Weak HDMI details for more information.
CPU Strapping issues
LSE Pin 16 GPIO_I2S_FRM Strapping issue details
This issue is fixed with the MinnowBoard Turbot: level shifters for the LSE are now enabled by the reset signal.
USB
The USB back powered issues are resolved on the MinnowBoard Turbot. However, the issues concerning USB 3.0 and 2.4GHz dongles may not be, see Back powered through USB details for more information.
Board Design Files
NOTE: All design files are released under Creative Commons CC-BY-SA (http://creativecommons.org/)
The MinnowBoard Turbot is intended to comply with all requirements and guidelines set forth by the Open Source Hardware Association (http://www.oshwa.org/)